Autobiography vs Biography
In the world of literature, storytelling is an art that transcends time and culture. The way we share the stories of our lives or narrate the lives of others has changed over centuries, evolving into rich, varied formats that capture the essence of human experience. Two of the most popular genres within life writing are autobiographies and biographies. While they both offer a glimpse into a person’s life, their distinctions are vital to understand for readers, writers, and aspiring authors alike.
This article will delve into the differences between autobiographies and biographies, the unique features of each, and guide you on which format might be best for your story or research.
What is an Autobiography?
An autobiography is a self-written account of a person’s life. It is narrated from the first-person perspective, which gives readers a personal and intimate look at the author’s experiences, thoughts, and emotions. Often, autobiographies are published by people who have led remarkable lives or made significant contributions in their fields. Through their own words, readers get direct insight into the author’s journey.
Key Elements of an Autobiography
- First-Person Narrative: Written in “I” form, making it a direct and personal account.
- Chronological Flow: Often follows a chronological sequence, from the writer’s early years to later life events.
- Focus on Personal Growth: Autobiographies typically explore personal development, life lessons, and inner growth.
- Detailed Life Events: They include pivotal moments and challenges that shaped the author’s life.
- Reflective Tone: An autobiographical work often reflects on past choices and experiences, offering insights and introspections.
Some well-known autobiographies include The Story of My Life by Helen Keller and The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank.
What is a Biography?
A biography is an account of someone’s life written by another person. Unlike an autobiography, it is written in the third person, giving an objective view of the subject’s life. Biographers extensively research their subjects to provide a detailed, fact-based narrative. A biography not only tells the story of a person’s life but also examines the societal context that shaped their experiences and achievements.
Key Elements of a Biography
- Third-Person Perspective: Written from an external viewpoint, allowing a broader scope of detail and context.
- Research-Based: Biographies are based on thorough research, including interviews, documents, and other sources.
- Objective Tone: Provides a balanced and factual representation, though some interpretation may occur.
- Broader Context: Often covers the societal and historical backdrop of the subject’s life.
- Comprehensive Detailing: Biographies may explore the person’s impact on their field, influence on others, and legacy.
Popular biographies include Steve Jobs by Walter Isaacson and Alexander Hamilton by Ron Chernow.
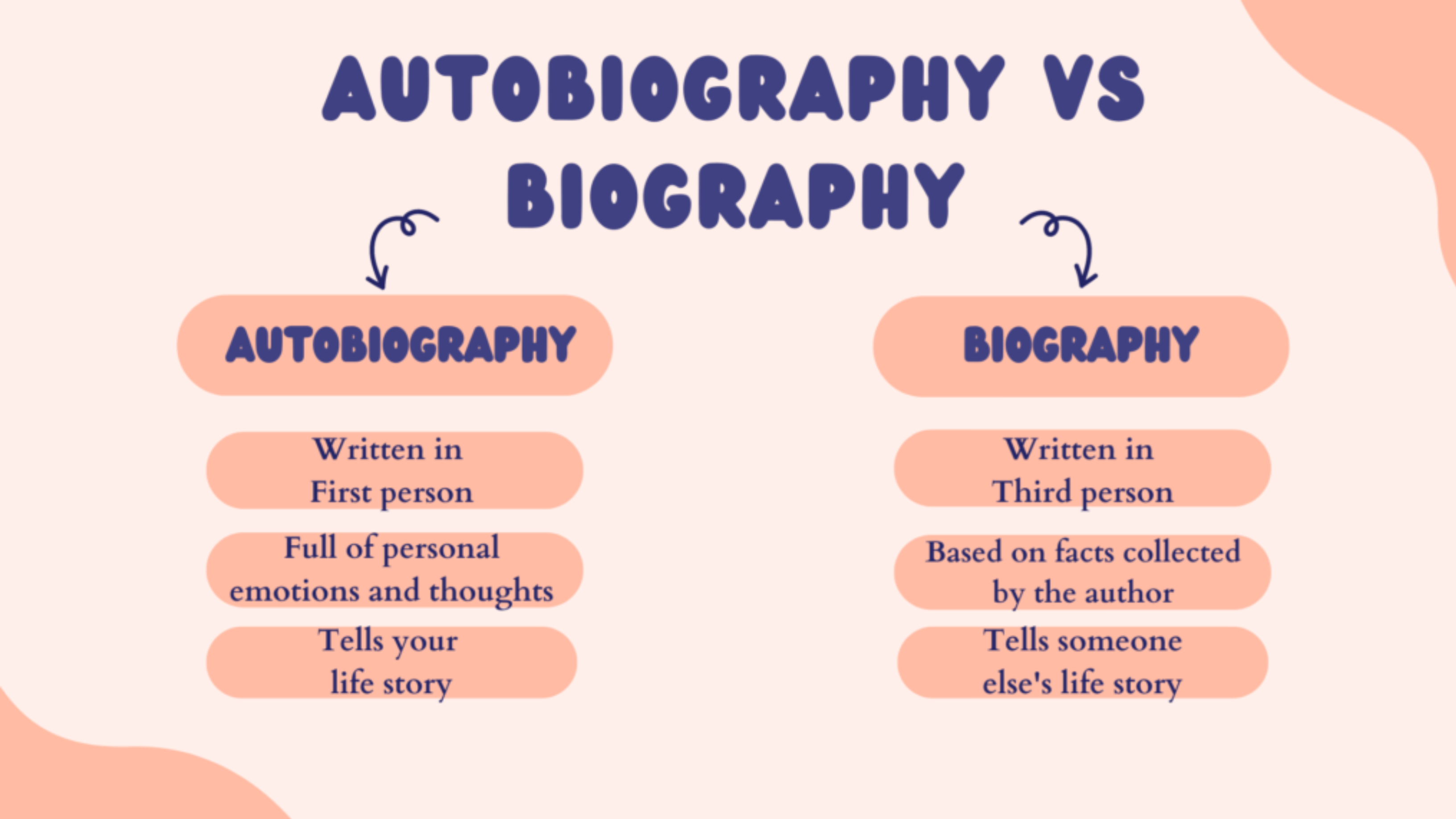
Key Differences Between Autobiography and Biography
While both forms seek to inform and engage readers about a person’s life, several distinctions set autobiographies and biographies apart. Here’s a closer look at these differences:
1. Authorship
- Autobiography: Written by the subject themselves.
- Biography: Written by someone other than the subject.
2. Perspective and Point of View
- Autobiography: Uses a first-person perspective, giving a subjective view of life events.
- Biography: Employs a third-person perspective, offering a more objective lens.
3. Purpose and Intent
- Autobiography: Often aims to share the subject’s personal experiences, inner thoughts, and reflections.
- Biography: Seeks to present a factual, balanced view, often focusing on the subject’s public achievements and influence.
4. Emotional Tone
- Autobiography: Tends to be more introspective and personal, as the author reflects on their life.
- Biography: Can maintain a neutral, fact-driven tone with emotional depth depending on the biographer’s approach.
5. Research Depth
- Autobiography: Generally relies on the author’s memory and personal records.
- Biography: Involves comprehensive research from various sources, such as interviews, archival documents, and letters.
When to Choose an Autobiography
Writing an autobiography might be the right choice if you:
- Want to share your personal experiences and reflections directly.
- Have gone through unique, life-changing events that may inspire others.
- Wish to provide an intimate account of your journey in your own words.
Autobiographies are often chosen by those who feel a personal connection to their readers. Celebrities, public figures, and inspirational individuals often write autobiographies to connect with their audience and share their experiences authentically.
When to Choose a Biography
Opting for a biography could be ideal if:
- You want to tell the life story of another person whose experiences or accomplishments are worth documenting.
- You enjoy researching and uncovering unknown or lesser-known details about someone’s life.
- You wish to provide an analytical and objective viewpoint on someone’s life and impact.
Biographies serve to educate, inform, and sometimes even challenge the way we view public figures. They are perfect for writers who enjoy digging deep into historical contexts and presenting a well-rounded picture of their subject.
Popular Subgenres of Life Writing
Both autobiographies and biographies come with their own subgenres, which add layers of variety to life writing. Let’s explore some popular subgenres:
1. Memoir
A memoir is a type of autobiography that focuses on specific periods or experiences in a person’s life rather than covering their entire life story.
2. Literary Biography
This is a biography that approaches the subject with a narrative, literary style, focusing on their personal struggles, relationships, and achievements.
3. Personal Narrative
Often overlaps with memoir, personal narratives are first-person stories about specific events in an individual’s life, emphasizing emotional experience over factual detail.
Benefits of Reading Autobiographies
Reading autobiographies offers numerous benefits. These firsthand accounts:
- Provide Insight: Get a glimpse into the author’s mind, understanding their motivations and values.
- Encourage Empathy: Learn from the personal struggles and triumphs of others, promoting empathy.
- Inspire Growth: Many autobiographies explore themes of resilience, ambition, and personal growth.
Benefits of Reading Biographies
Biographies also hold unique benefits, such as:
- Broad Perspective: Biographies present the subject within a larger societal and historical context.
- Educational Value: Through meticulous research, biographies educate readers about the time periods and environments the subjects lived in.
- Objective Insights: Biographies provide a balanced view, presenting both achievements and failures.
Conclusion
In summary, autobiographies and biographies each offer distinctive ways to capture and share life stories. Autobiographies are deeply personal, told by the individuals themselves, whereas biographies are detailed accounts crafted through careful research by someone else. Whether you’re an avid reader or an aspiring author, understanding these differences can help you choose the best format to explore or tell a life story.
If you’re considering writing a life story—be it your own or someone else’s—think about the purpose, perspective, and style that would best convey the journey. Both autobiographies and biographies have the power to educate, inspire, and leave a lasting impact on readers, making them enduring pillars in the world of literature.
Read More :-
-
Catherine the princess of wales the biography : A Biography of a Modern Royal Icon
-
Shai Hope IPL 2024 : A Rising Star Ready to Shine
-
Shai Hope Net Worth : Earnings, Lifestyle, and Career Highlights